The average monthly gross pay in Slovenia stood at EUR 1,851 in 2019, which is 4.1% more than the year before. The figure was higher than the national average for men and lower for women. A total of 64.4% employees got lower pay than the average, the Statistics Office announced this week.
Last year, the average monthly gross pay of men was 2.7% higher than the average and amounted to EUR 1,901. Among women, the figure was 3.3% lower than the average and totalled 1,790 euros.
For 63.2% of employees, the 2019 net pay was lower than the average. The monthly net pay median, which divides the population into two equal parts, was set at EUR 1,026.
The average monthly net pay was lower than EUR 790 for 25% of people, higher than EUR 1840 for 10% of people and higher than EUR 3505 for just 1%.
slovenia pay by occupation job work.png
Last year, only employees in the central Osrednjeslovenska statistical region received an above-average monthly gross pay, which was 11.1% higher and amounted to EUR 2,056.
The lowest average pay was recorded in the Primorsko-Notranjska region, standing at EUR 1,598, down 13.7% on the average.
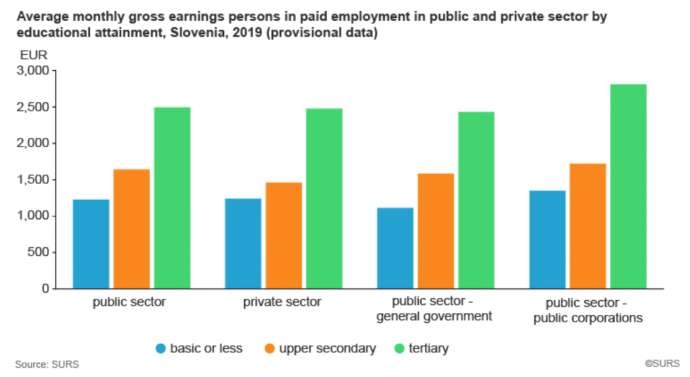
In 2019, the average monthly gross pay of persons with tertiary education in the public sector was roughly on par with the figure in the private sector.
The former received EUR 2,434 and the latter EUR 2,478. Persons in paid employment with this level of education in public corporations received much higher average monthly gross earnings though (EUR 2,812).
Among employees with secondary education, those employed in the public sector had a slightly higher average monthly gross pay than those employed in the private sector. The opposite was true for employees with only basic education.
In the public sector, the gap between the average monthly gross earnings of women and men was the smallest for persons with tertiary education – a 20.1% gap.
Meanwhile, men with secondary education in the public sector received a 25.9% higher average monthly gross pay than women, while men with only basic education received a 21.3% higher figure compared to women.
In the private sector, the pay gap between women and men in secondary education averaged 15.8% in favour of men. It was highest among employees with tertiary education – a 22.2% gap.
In public corporations, the average monthly gross pay of men with basic education was 28.6% higher compared to women, while this difference was slightly lower among persons with secondary or tertiary education – men received about 25% higher average monthly gross pay than women.